Researcher WANG Difeng and his collaborators published a paper entitled "A New High-Resolution Remote Sensing Monitoring Method for Nutrients in Coastal Waters" in the well-known journal IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing in the field of remote sensing. The first author of the paper is HUANG Jingjing, a doctoral student jointly trained by our laboratory and Zhejiang University. The corresponding author is researcher WANG Difeng of our laboratory. The collaborators include LI Hongzhe, a master's student jointly trained by Shanghai Jiao Tong University and our laboratory, researcher HE Xianqiang of our laboratory, researcher BAI Yan and senior engineer GONG Fang.
Marine aquaculture is an important offshore economic activity, and excessive aquaculture may lead to the deterioration of marine ecosystems. The concentration of nutrients (mainly dissolved inorganic nitrogen (DIN) and active phosphate (PO4)) in aquaculture sea areas is the main factor characterizing the health of the sea area. Traditional on-site monitoring methods have limitations in time and space, while remote sensing technology has the advantages of high spatial coverage and long-term sequence monitoring. However, the current difficulty in estimating nutrient concentration with high spatial resolution remote sensing mainly lies in the small amount of matching data and the algorithm The accuracy needs to be improved, etc.
This study takes Dayu Bay, Cangnan County, Wenzhou, as the main research area (Figure 1), where kelp cultivation has been carried out for a long time. In order to solve the problem of small amount of matching data, the dual-star combination (Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3) method is innovatively solved. The Sentinel-3 L2 level data covering Wenzhou offshore was matched with the field measurement data. Then, the spectral correspondence between Sentinel-2 (after atmospheric correction) and Sentinel-3 was converted to obtain the relationship between the Sentinel-2 band and the field measurement data. matching data set. Compared with Sentinel-2, which can only match data from 10 stations when matched with measured data alone, the number has been increased to 112 through the dual-star combination method, which greatly increases the amount of matching data.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of Dayuwan research area
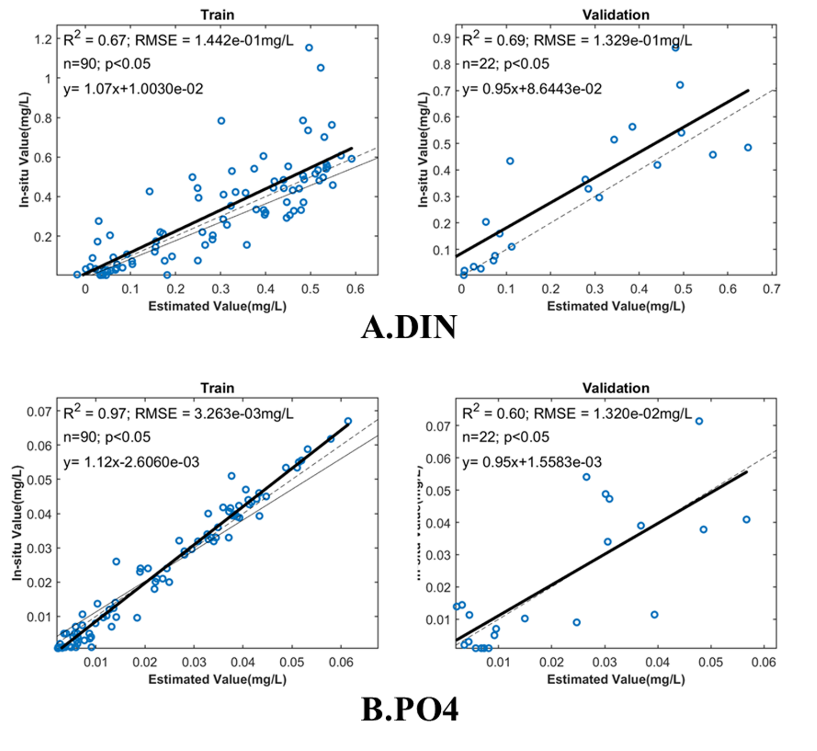
In response to the problem that the accuracy of the algorithm needs to be improved, this study used machine learning algorithms (including support vector machines and Gaussian regression models) to build an inversion model with an independent verification process. In order to prevent overfitting, a 5-fold cross-validation was used. The RMSE of the inorganic nitrogen model validation set was 0.13mg/L, the RMSE of the active phosphate validation set was 0.013mg/L, and R2 was greater than 0.6 (Figure 2). The model was applied to obtain long-term changes in nutrient concentration in Dayu Bay, as well as the average nutrient concentration in different seasons (Figure 3). Overall, the nutrient concentration in Dayu Bay is high in winter and low in summer.
Figure 2. Model accuracy scatter plots
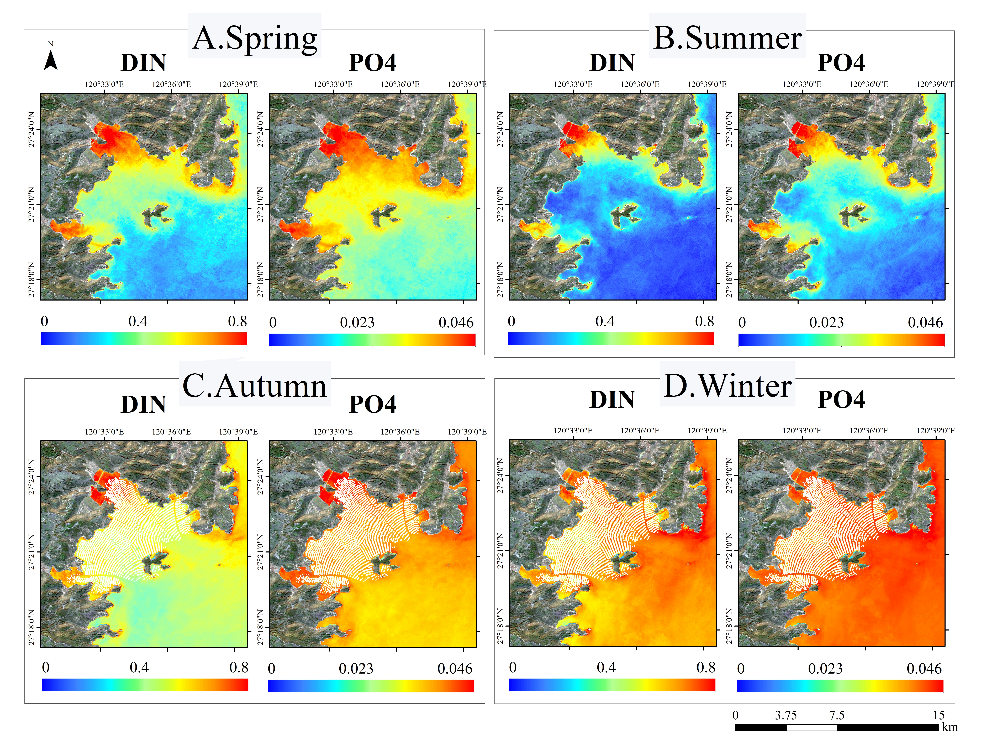
Figure 3. Distribution of nutrient concentration in Dayu Bay in different seasons
On this basis, in order to analyze the regulatory mechanism of nutrient changes, the changes in aquaculture rafts and precipitation were analyzed. Extracting the area information of culture rafts from remote sensing images, it was found that culture rafts in Dayu Bay generally appear at the end of September and early October every year, almost completely disappear in mid-March of the following year, and the number reaches a maximum in December. Combined with the nutrient salt inversion results, it was found that the concentration of nutrient salts during the breeding period was significantly greater than during the non-breeding period. Based on the precipitation in Wenzhou, which is mainly concentrated in summer (June to August) and the precipitation in each month, the overall nutrient concentration is positively correlated with the area of the breeding raft, negatively correlated with the precipitation, and has a correlation with the area of the breeding raft. Stronger than the correlation with precipitation (Fig. 4).
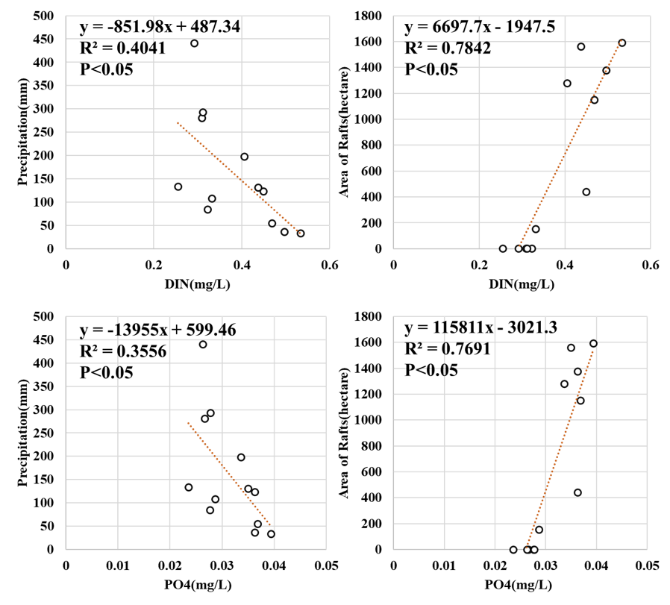
Figure 4. Relationship between nutrient concentration, culture raft area and precipitation
This study achieved high spatial resolution remote sensing monitoring of nutrients in coastal waters, provided the changing characteristics of nutrient concentrations in Dayu Bay from 2015 to 2022, and conducted a preliminary analysis of its changing mechanisms, providing a basis for high-resolution remote sensing. The practical application in offshore breeding environment monitoring provides a new idea. As one of the main components of the achievement "High-resolution sewage discharge into the sea and offshore water quality satellite remote sensing monitoring technology", the related technology was selected into the list of "Top Ten Scientific and Technological Innovations for Ecological Environment in Zhejiang Province in 2023" and was used during the sailing competition of the 2023 Asian Games. Providing technical support for marine environment quality assurance tasks is an important measure for scientific research to support local development.
Citation:
Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Pan, S.; Li, H.; Gong, F.; Hu, H.; He, X.; Bai, Y.; Zheng, Z. A New High- Resolution Remote Sensing Monitoring Method for Nutrients in Coastal Waters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing 2023, 61, 1–15, doi:10.1109/TGRS.2023.3294436.